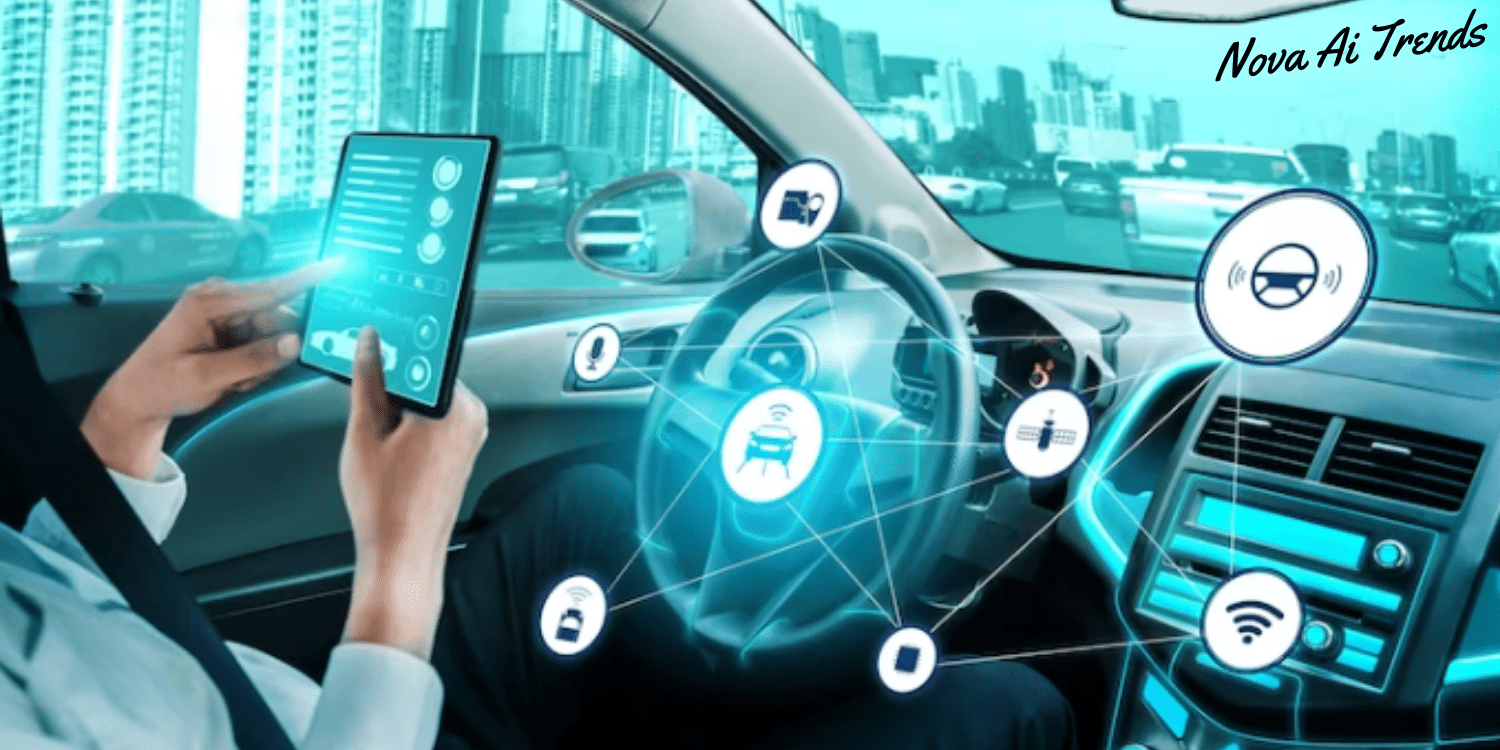
AI in Autonomous Vehicles: Driving into the Future
Envision a future where your daily travel doesn’t require navigating through congested traffic, but instead offers the luxury of sipping coffee, indulging in a good book, or being productive while your self-driving vehicle autonomously escorts you to your chosen destination. This captivating prospect is rapidly materializing due to the incorporation of AI in autonomous vehicles. This article will explore the fascinating odyssey of AI in self-driving automobiles, its current status, the obstacles it encounters, and the vast potential it possesses to transform the realm of transportation.
The Evolution of Autonomous Driving
The aspiration for self-driving cars has traveled a significant distance since its inception with Carnegie Mellon University’s Navlab prototype in the 1980s. Advanced AI methodologies, such as computer vision, machine learning, and sensor fusion, have transformed autonomous vehicles from mere ideas into practical realities. Pioneering corporations like Waymo, and Tesla, and established automakers have heavily invested in advancing autonomous driving innovations.
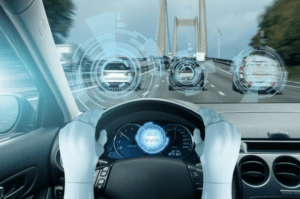 AI serves as the core engine propelling the functioning of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles depend on an assortment of sensors, encompassing LIDAR, radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors, to gather information about their immediate environment. In real-time, AI algorithms meticulously analyze this data, determining actions like acceleration, braking, and steering, even forecasting the behaviors of other vehicles sharing the road. The remarkable capability to adjust and acquire knowledge from experience stands out as a defining characteristic of AI-driven autonomous vehicles.
AI serves as the core engine propelling the functioning of autonomous vehicles. These vehicles depend on an assortment of sensors, encompassing LIDAR, radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors, to gather information about their immediate environment. In real-time, AI algorithms meticulously analyze this data, determining actions like acceleration, braking, and steering, even forecasting the behaviors of other vehicles sharing the road. The remarkable capability to adjust and acquire knowledge from experience stands out as a defining characteristic of AI-driven autonomous vehicles.
AI Technologies Paving the Way
Computer Vision: Computer vision empowers autonomous vehicles to perceive and understand their environment. It encompasses functions such as identifying objects, discerning road signs, and recognizing pedestrians, and other vehicles, all while grasping their spatial connections. Advanced deep learning algorithms, notably Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have played a pivotal role in substantially enhancing the accuracy of object detection and image classification.
Machine Learning: Machine learning forms the essence of autonomous vehicles, empowering them to acquire knowledge from their encounters and refine their decision-making prowess over time. Particularly, reinforcement learning assumes a vital role, guiding the vehicle through intricate scenarios by providing rewards for making sound decisions.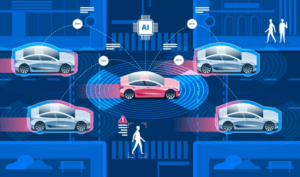
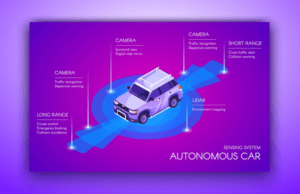
Sensor Fusion: Autonomous vehicles depend on an amalgamation of sensors, encompassing cameras, LIDAR, radar, and ultrasonic sensors. AI is used to merge data from various sensors, creating a comprehensive and precise vehicle environment representation. The fusion of sensors stands as a critical element in securing resilient and dependable autonomous driving capabilities.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP technology is used to enable human-vehicle interaction. Voice recognition and natural language understanding allow passengers to communicate with their autonomous vehicles, giving instructions to change routes, adjust climate control, or engage in friendly conversation.
Challenges on the Path to Autonomy
While the advancements in AI for autonomous vehicles are remarkable, they are accompanied by challenges:
Safety and Regulation: Ensuring the safety of autonomous vehicles is paramount. The development of comprehensive safety and operational guidelines by governments and regulatory bodies is still an ongoing process.
Data Privacy and Security: The extensive data generated and processed by autonomous vehicles raises concerns about data privacy and cybersecurity. Unauthorized access to a vehicle’s systems could pose serious risks.
Ethical Quandaries: AI in autonomous vehicles confronts intricate ethical predicaments. For example, a self-driving car faces a dilemma: collide with a pedestrian or swerve into another lane, risking its passengers’ safety. The resolution of these ethical dilemmas represents a pivotal challenge.
Public Perception: Public trust in self-driving technology remains a significant hurdle. High-profile accidents and concerns about job displacement in the transportation industry have contributed to skepticism about autonomous vehicles.
Unlocking the Potential of Autonomous Vehicles
Even with the existing challenges, the prospective advantages of AI in autonomous vehicles are undeniably significant:
Enhanced Safety: Human errors are responsible for most accidents on the road. Autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce accidents by eliminating driver error. They can also detect and respond to potential hazards much faster than a human driver.
Reduced Traffic Congestion: Self-driving cars can communicate with other vehicles and traffic infrastructure, improving traffic flow. Consequently, this can lead to decreased traffic bottlenecks and expedited journey durations.
Enhanced Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles present transportation options tailored for individuals with disabilities, seniors, and those unable to drive. This transformative potential has the power to revolutionize mobility for those currently reliant on others for transportation.
Environmental Benefits: Autonomous vehicles may cut carbon emissions and fuel use by enhancing driving efficiency and curbing traffic congestion.
Economic Impact: The development and deployment of autonomous vehicles can have a profound economic impact, creating new industries such as vehicle software and maintenance and potentially reducing transportation costs for businesses.
The Current State of Autonomous Vehicles
 Based on my last update in September 2021, the evolution and rollout of autonomous vehicles continued to progress. Corporations such as Waymo, Tesla, and Uber were actively trialing their autonomous vehicles on public roads, achieving varied levels of success. Notably, Tesla had launched its “Full Self-Driving” (FSD) package in a beta version for a select group of its clientele, even if it hadn’t achieved full autonomy at that point.
Based on my last update in September 2021, the evolution and rollout of autonomous vehicles continued to progress. Corporations such as Waymo, Tesla, and Uber were actively trialing their autonomous vehicles on public roads, achieving varied levels of success. Notably, Tesla had launched its “Full Self-Driving” (FSD) package in a beta version for a select group of its clientele, even if it hadn’t achieved full autonomy at that point.
It’s essential to acknowledge that the state of autonomous vehicles may have evolved since then. Regulations, public perception, and technological advancements play pivotal roles in shaping the progress of autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
AI in autonomous vehicles marks a groundbreaking technological advancement with the potential to revolutionize our approach to transportation. Despite the persistent hurdles and apprehensions, the advantages, including heightened safety, alleviating traffic congestion, and enhanced accessibility, hold great appeal. A challenging journey to full autonomy promises a future of productive, secure, and efficient commutes. As technology continually advances, we can eagerly anticipate captivating developments on this transformative journey to autonomy.









